In this article we will talk about calcium -containing products, which should definitely include in your diet, but correctly balancing it.
Contents
- What is the content of calcium in milk and dairy products: table
- High calcium content in hard cheeses
- Calcium content in seeds and nuts: table
- What is the content of calcium in poultry products?
- Fish products and seafood are also rich in calcium content: average value
- Legumes and calcium content: table
- Spices and spices that are rich in the content of calcium in their composition: table
- Low calcium content in vegetables and herbs: Table
- Calcium content in fruits and berries: table
- Calcium content in grain crops: table
- Calcium content in meat products
- Daily calcium consumption for women and men
- What products worsen the absorption of calcium?
- Video: where is the high content of calcium?
Calcium is the main building element of our bone system, which takes part in many processes. And its role in the body is difficult to overestimate, because it is responsible not only for tooth enamel, but also for the nervous, heart and blood systems. Therefore, it is so important to know in which products the content of calcium in large or optimal quantities, as well as in what form the mineral is best absorbed.
What is the content of calcium in milk and dairy products: table
All products can be conditionally divided into those that have a high calcium content; in which calcium is not very much, but it is in the most assimilated form; And on those in which calcium is not enough or not at all. Consider the main products on the chronology of this classification. But let's not forget that the indicator of calcium milligrams in a particular product is only the first starting point, which in itself is not a determining factor.

Milk and its derivatives are the main, popular and most affordable suppliers of calcium to the body that can provide daily need in this trace element. The ratio of calcium content per 100 g of the product:
| Cottage cheese | 160-100 mg |
| Sour cream | 85-90 mg |
| Yogurt | 112-124 mg |
| Fatfound yogurt | up to 180 mg |
| Buttermilk | 115 mg |
| Kefir | 120 mg |
| Milk cow | 113-120 mg |
| Goat milk | 134 mg |
| Serum | 103 mg |
| Loof dry milk | as many as 1155 mg |
| Condensed milk | 284 mg |
Important: thanks to lactose, calcium contained in dairy products, has good digestibility. But it is it that causes intolerance to some people, so these products are not suitable for everyone.

High calcium content in hard cheeses
All records beat hard cheeses - the highest calcium content.
Despite the fact that these are also dairy products, but they require a separate group. True, it is worthwhile to understand in which cheeses the calcium content is on the peak limit:
- Parmesan leads in this nomination - 1184 mg
- Pecorino Romano has 1067 mg salty cheese
- Gruyer - 1011 mg
- Chedder and Dutch containing calcium slightly less - 1000 mg
- Mozarella - 730 mg
- Swiss - 890 mg
- Gauda - 720 mg
- Suluguni - 650 mg
- There are only 530 mg in Brynze
- Adyghe cheese is even lower - 520 mg
- But the smallest calcium content in creamy cream cheese is 425 mg
So, for example, breakfast from a piece of Parmesan cheese and a glass of yogurt is able to provide the daily need for the body in calcium.
Important: dairy products have such a feature - the lower the percentage of fat content, the higher the calcium content. But such an element is much worse absorbed than in fatty varieties.

Calcium content in seeds and nuts: table
This is a real storehouse of calcium, which is in these products in the most assumed form. The following products are especially rich in calcium:
- Mac - 1460 mg
- Sesame - 977 mg
One teaspoon of these seeds with more than enough to satisfy the daily need of an adult for calcium. The only reservation is sesamera, just like a poppy, they do not eat spoons, but are used mainly in baking. Therefore, to replenish the body with calcium, other seed products with a ratio of 100 g are recommended:
| Hazelnut | 288 mg |
| Hazel | 225 mg |
| Flax seeds | 255 mg |
| Hazelnut | 188 mg |
| Pistachios | 105 mg |
| Walnut | 89 mg |
| Sunflower seeds | 78 mg |
| Peanuts have the smallest content | 60 mg |
| A lot of calcium and in the almond | 273 mg |
Important: folic acid, which is in the almond, is capable of not only violating the balance, but also washing calcium from the body. Therefore, it is impossible to get involved in it.

What is the content of calcium in poultry products?
- The largest calcium content is noted In egg powder- 193 mg
- The second in this indicator is Chicken yolk- 136 mg
- But In general, chicken eggcontains only 55 mg of calcium per 100 g of weight.
It should be recognized that this indicator is relatively high. Moreover, from eggs you can get valuable protein and other important minerals!
Fish products and seafood are also rich in calcium content: average value
We repeat that the content of calcium does not give guarantees for the proper replenishment of calcium reserves. The accompanying elements play a fairly important role, like magnesium or vitamin D. Therefore, it cannot be said that only dairy products or seeds need to be eaten. And for this we go further and look at the products, albeit with a smaller, but “light” calcium.
Contrary to the widespread opinion that red fish contains a lot of calcium, this is not so:
- Gorbusha - 20 mg;
- Keta - 20 mg;
- And salmon is even 15 mg per 100 g of the product
Important: as we see, they are not at all record holders for the content of calcium among marine products. But they have a large number of Vitamin D,due to which the calcium, in them contained, is absorbed by the body completely.
- But red granular caviar gives the body 90 mg of calcium. Moreover, it is more in it and vitamin D, as well as its influence on digestibility is not inferior to fish.
The greatest content of calcium among marine representatives per 100 g is:
| Sardine Atlantic, canned goods with bones | 383 mg |
| Sweeped bream | 274 mg |
| Canned stavride | 243 mg |
| Anchovies in oil | 232 mg |
| Gorbusha in canned goods | 185 mg |
| Baked pike perch | 141 mg |
| Hot smoking perch | 150 mg |
| Sea bass | 120 mg |
| River perch | 103 mg |
| Shrimps | 91 mg |
| Oysters | 82 mg |
| Herring | 74 mg |
| Baked trout | 55 mg |
| Media | 50 mg |
| Squids | 40 mg |
Important: small sea fish also not contain a lot of calcium (approximately 50 mg per 100 g of the product). But in ready -made canned foods, for example in sprats, its maintenance is already 300 mg per 100 g of the product. But do not forget that the bones of the monastery, which are soft enough for food and digestion, are accounting.
Of course, all sea or river representatives are a valuable food product. But as well as red fish, not due to the high content of calcium, but due to its optimal balance with vitamin D and enrichment with polyunsaturated fatty acids Omega-3 and Omega-6, which are not produced by the human body.
Dried seaweed are very rich in calcium:
- agar contains 625 mg of calcium per 100 g
- raw agar - 54 mg
- dried sea cabbage - 205 mg
- raw cabbage product - 168 mg

Legumes and calcium content: table
Bobov, characterized by a high calcium content, should be attributed to Soy.
- But it is the largest percentage of calcium in soy cheese of tofu - 282 mg
- At a pace - 11 mg
- Its dry beans contains 201 mg calcium
- In boiled form, this percentage drops to 102 mg
Important: but there is a lot of phytic acid in Soy, which affects the balance of trace elements. To neutralize all the soil should be soaked at night in the water before cooking.
Bob cultures for 100 g:
| Mash | 192 mg |
| The beans are white | 190 mg |
| Lentils | 83 mg |
| The beans are red | 71 mg |
| Chicker dry | 57 mg |
| Lupine beans | 51 mg |
| Dry peas | 50 mg |
| Green beans | 44 mg |
| Green peas canned | 20 mg |

Spices and spices that are rich in the content of calcium in their composition: table
The list of groups of products is completed, which have a fairly high content of calcium, spices. Of course, it will not work to eat them with spoons, but when adding to food, you will receive the necessary supply. That is why, despite impressive numbers, they cannot be called full -fledged calcium leaders. Attitude to 100 g:
| Marjoram | 1990 mg |
| Oregano dried | 1597 mg |
| Dill seeds | 1567 mg |
| Cinnamon | 1002 mg |
| Bay leaf | 884 mg |
| Allspice | 661 mg |
| Black pepper | 443 mg |
| chili pepper | 330 mg |
| Nutmeg | 252 mg |
| Turmeric | 168 mg |
| Salt | 24 mg |
| Cheese ginger | 16 mg (dry form - 116) |
| Apple vinegar | 7 mg |

Low calcium content in vegetables and herbs: Table
Despite the fact that some components may contain a lot of calcium, but they have additional elements, which can block the digestibility of calcium. Therefore, all of the following groups of products belong to a low or poorly learned calcium percentage. But then they have many other useful vitamins and macro elements.
Important: for example, in green leaves there is oxalat. It blocks calcium and makes it inaccessible. Therefore, even a large amount of greens is not able to saturate the body with the proper daily rate of calcium. But cabbage is an exception in this matter.

No matter how surprising, vegetable crops have a fairly high indicator of calcium content in its composition. True, in comparison with other gifts of our gardens, ordinary greens, growing in summer in the beds, are most rich in calcium. Content for 100 g of product:
| Parsley leads not only vitamins | 245 mg of calcium |
| Dill contains | 223 mg |
| Young leaves of dandelion | 187 mg |
| Garlic | 181 mg |
| Basil | 177 mg |
| Curly cabbage | 150 mg |
| Spinach | 106 mg |
| Cabbage | 105 mg |
| Maslins | 94 mg |
| Corses Salata | 81 mg |
| Leaf salad | 77 mg |
| Green onion | 57 mg |
| Broccoli | 47 mg |
| Sorrel | 44 mg |
| Carrots and turnips | 30 mg |
| Radish | 25 mg |
| Onion | 23 mg |
| Cucumber and tomato | 15-14, respectively |
| Bulgarian pepper | 10 mg |
| Potato | 6 mg |
| Corn | 3 mg |
Important: nettle has a very high calcium content - 713 mg per 100 g.
We can conclude that there is a lot of calcium in green and leaf gifts of the earth.

Calcium content in fruits and berries: table
Fruits for the mass are not particularly rich in calcium. But there are small exceptions. Naming for 100 g:
| Goji berries | 190 mg |
| Dried figs | 162 mg |
| Dates | 64 mg |
| Dried apricot | 55 mg |
| Black currant | 55 mg |
| Raisin | 53 mg |
| Orange | 40 mg |
| Mulberry | 39 mg |
| Grape | 37 mg |
| Kiwi | 34 mg |
| Persimmon | 27 mg |
| Raspberry | 25 mg |
| Dried bananas | 22 mg (fresh - 9) |
| Strawberries and cherries | 16 mg |
| Quince | 11 mg |
| Pomegranate | 10 mg |
| Watermelon | 7 mg |
| Melon and peach | 6 mg |
It is worth noting that the content of calcium is larger in dried fruits than in a fresh product.

Calcium content in grain crops: table
Although calcium indicators seem good at first glance, we are talking about products in dry form. When cooking, this mass fraction falls significantly. The relatively high calcium content is observed in such grain crops per 100 g:
| Barley grits | 80 mg |
| Buckwheat | 70 mg |
| Oat groats | 64 mg |
| White bread | 53 mg |
| Wheat groats | 40 mg |
| Rice | 40 mg |
| Bulgur | 35 mg |
| Rye bread | 30 mg |
| Buckwheat | 25 mg |
| Bread from bran | 23 mg |
| Corn grits | 20 mg |
| Sunny | 18 mg |
| Pearl barley | 15 mg |
Important: in multizer bread for 100 g, a fairly high indicator is 238 mg. But the lightweight will make you eat a lot of the product.

Calcium content in meat products
Most meat products are not a full -fledged source of calcium. The greatest content is noted in the beef scar - 81 mg.
Meat products that are more widely used in nutrition are already significantly inferior in calcium:
- Young veal - 24 mg per 100 g
- Pork fillet - 22 mg
- Rabbit- 19 mg
- Chicken meat and altogethercontains only 16 mg of calcium per 100 g of product
- Broilery chickens - 14 mg
- TURNING meat - 12 mg
That is, 100 g of these products contain only 1-2% of calcium from the daily norm of its consumption.
Important: Calcium is completely absent in animal fats, various oils and mushrooms.

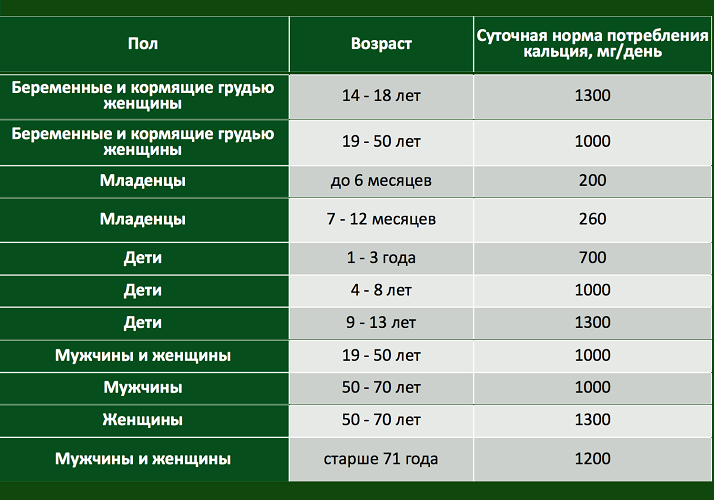
Daily calcium consumption for women and men
It is worth taking into account not only the content of calcium, but also the need for calcium, its daily norm.
The need for calcium depends on the age and ability of the body to absorb it.
- It is generally accepted that normally the daily dose of calcium intake in our body should be at least 1000 mgfor an adult and a child from 4 years of age.
- For teenagers at the age of 9-18 years, That is, during a period when the main formation of the skeleton and muscles occurs, this norm should be increased up to 1300 mg.
- The maximum dose of daily calcium consumption should be no more than 2500 mg. And do not forget that an excess of calcium can lead to serious disorders in the body in the work of the central, nervous and heart systems.
Important: it must be borne in mind that the assimilation of calcium depends not only on the concentration of calcium in food, but also on its balance with vitamin D, magnesium and other products that can affect the absorption of calcium.
Below in the picture a table of the daily norm of calcium for women, men, adolescents, children, infants and pregnant women is given.
What products worsen the absorption of calcium?
- For example, some species fat of animal origin or palm oil They have the ability to bind calcium ions, forming its unhappy form. And this leads to a deficiency of calcium!
- Animal proteins - eggs, pork meat, beef, especially red, birds, rabbit, lamb ( protein diets), protein remove calcium from other products that you eat, which leads to its deficit.
- Coffeef's drinks and carbonated affect the lack of calcium in the body.
- Laxatives and diuretics, alcoholism, smoking reduce calcium assimilation.
Derive calcium from the body:
- Refined products - Sugar, flour, white purified rice, white bread.
- Very salty products - fast foods, sausages, semi -finished products.
Because of this, the teeth begin to crumble, frozen nails and hair become, heart rhythm is disturbed, muscle cramps occur, which leads to various diseases.
In order to avoid a lack of calcium in the body, follow your nutrition.
The diet should have more products containing calcium than products that do not contain or inhibit assimilation.
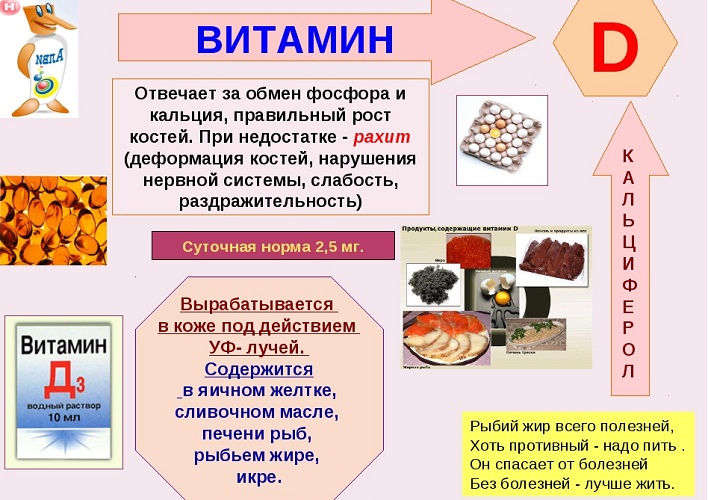
In addition, always use products with vitamin D (fish, cod liver, egg yolks) and be more on the street on sunny days, from sunlight the body produces vitamin D.
More about vitamin d Read the article.
Vitamin D3: Why do women need it, men, pregnant women, children, newborn, elderly people
Magnesium is needed for the absorption of calciumwhich you take from drinking water. Replace all drinks (especially sweet) clean drinking water and you will get a good dose of magnesium.
For perfect control over calcium levels in the body and its balance with other trace elements, the optimal solution will be analysis of blood biochemistryand Analysis for thyroid hormones(regulates the assimilation of calcium), which today can be done in any medical institution.
And do not forget to take vitamins with calcium, but only after consulting a doctor.







