The article will tell about the structure of the throat and everything that is connected with this.
Contents
Building and functions of the throat
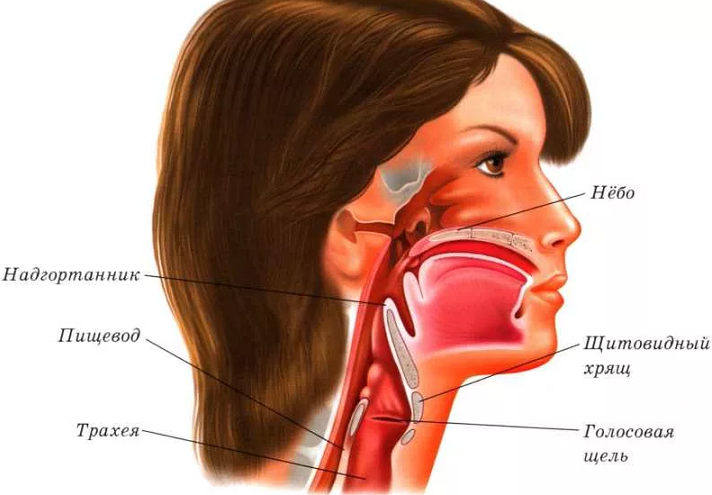
The throat belongs to one of the vital organs, is a conductor between the oral cavity and the nose on the one hand, as well as light and esophagus - on the other. Those. The throat is arranged in such a way that this makes it possible to move food to the esophagus, and the air - circulate in the lungs. This organ is a large number of necessary blood vessels, nervous and muscle tissues. The throat is mainly built from the larynx and pharynx.
These organs in the human body grow into the trachea. If the throat in our body is responsible for the movement of food and oxygen, then the larynx is necessary for the normal operation of the vocal ligaments. Thus, the throat is also responsible for human speech abilities.

The throat is a rather complex organ, which performs several functions in human life: respiratory, speech and transportation of food in the body.
And once again we repeat that the throat is built from other organs: pharynx and larynx. As we already understood, the throat serves as a conductor of food and air, so all the muscles included in it work very harmoniously, completely coordinating each other. And if these muscles suddenly begin to function not consistently, then this can even lead to fatal consequences, for example, there is a danger of food enters into the lungs. Thus, a person can simply suffocate.
In children and adults, the throat is approximately the same. The only difference is that in adults all the tubes are wider than in children. Therefore, for children, the throat disease can be quite dangerous, as it causes swelling in muscle tissues, thereby making it difficult to flow oxygen in the lungs. In general, it will be very useful to know how the throat is arranged - this will help to better take care of it with diseases and conduct diseases prevention.
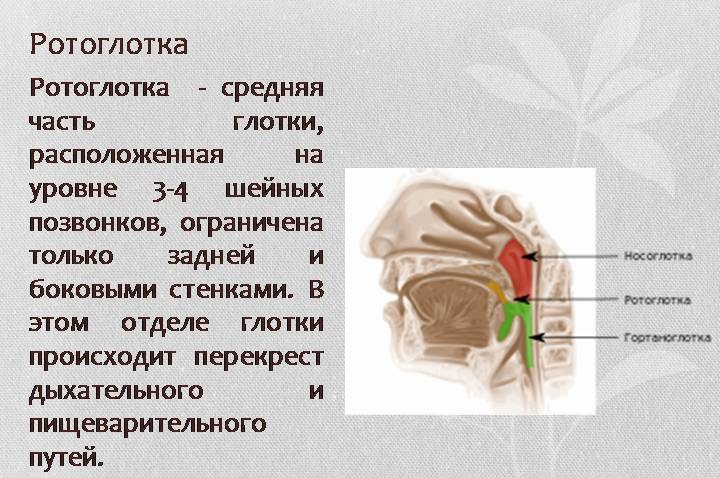
To begin with, the sip is divided into a nasopharynx and oropharynx.
Human sip: structure, functions
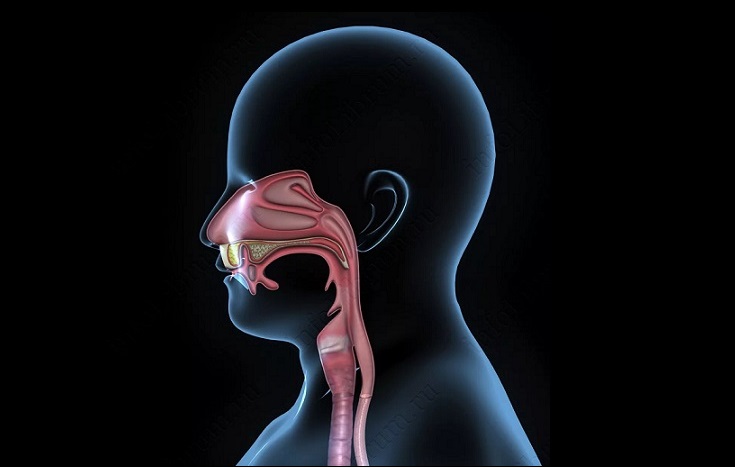
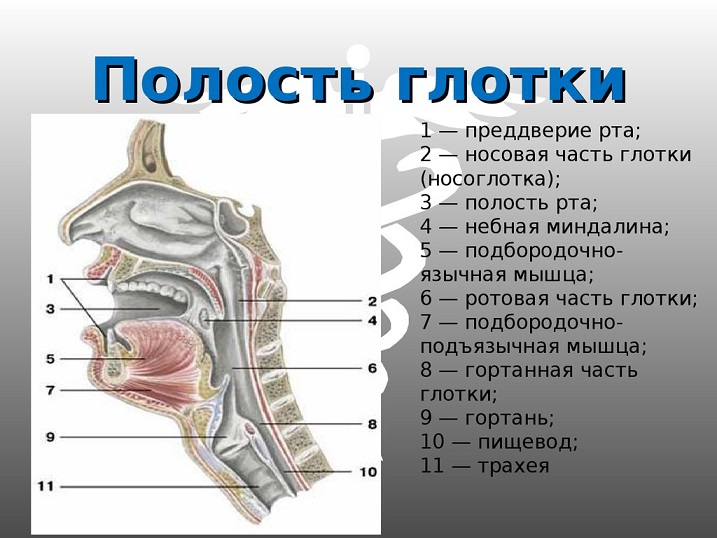
The sip, as part of the throat, has the shape of a cone, only the base up. It is formed behind the oral cavity. The upper section of this cone is wider than the lower. The pharyngeal cone is located in such a way that the pharynx has great strength. The lower compartment of the cone grows into the larynx. The larynx is outwardly shrouded in tissues of the muscles connecting to the oral cavity. This fabric performs its certain functions. There are glands on it that are responsible for moisturizing the throat during food or conversation.

The nasopharynx of a person
It was already noted above that the throat in the body is located so that it comes to other organs. Combining with the nose and oral cavity, the throat has a nasopharynx and oropharynx, respectively. First, let's talk about the first of them.
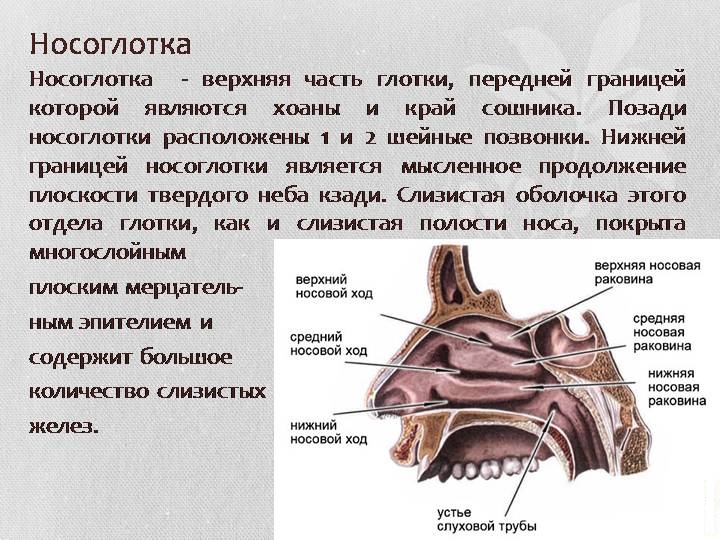
Nasopharynx - The component component of the pharynx is located in its upper part. Below it, you can observe a soft sky that rises up when swallowing. The sky covers the nasopharynx with such movements, which protects the latter from entering it (and, consequently, into light) foods. The upper nasopharyngeal wall has clusters of tissues called adenoids. This organ has a tunnel (Eustachian pipe), fastening the throat and middle ear.
Human oropharynx: structure, functions
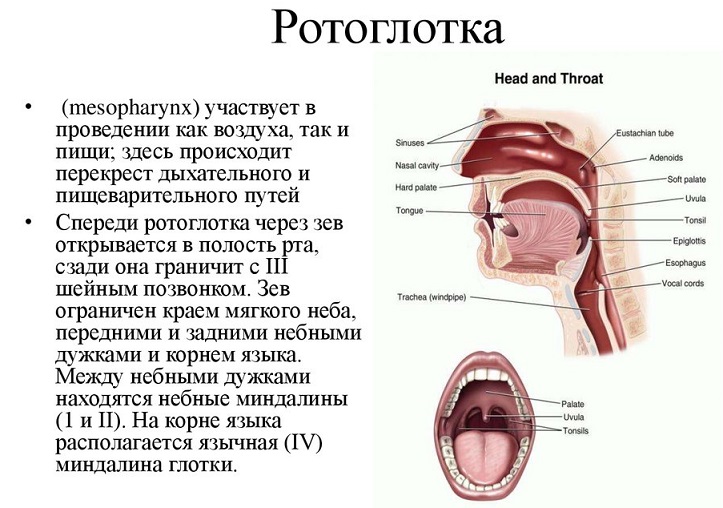
The second component component of the throat is a oropharynx. It is located immediately behind the oral cavity. It is responsible for conducting oxygen from the oral cavity further into the lungs. This organ is more mobile than the nasopharynx. Such mobility is necessary for a person to speak freely when all the corresponding muscles are involved for this.
Thus, we found out that the throat is built from certain components, which, in turn, also have various components, we will not go much in them. Let's just say that such components include, for example, a language due to which a person can speak and feel the taste of food. You can also note the tonsils - organs that are very susceptible to diseases (colds, etc.).
Human larynx: structure, functions
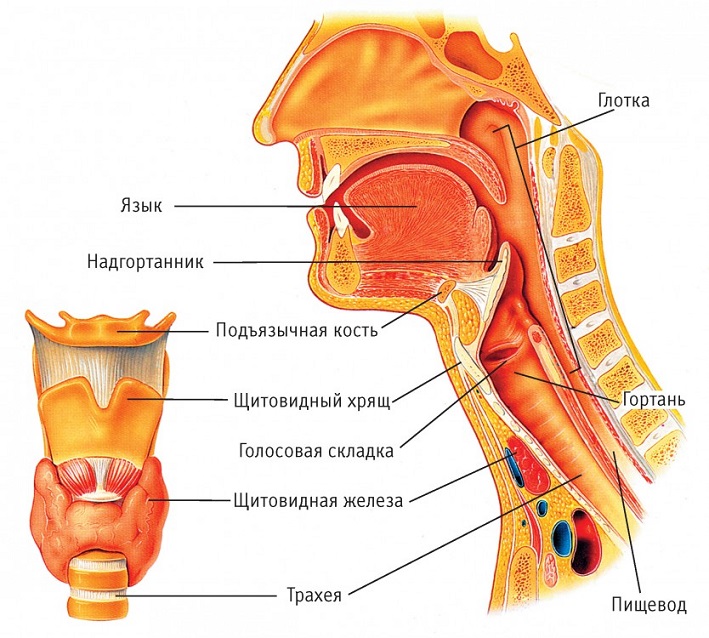
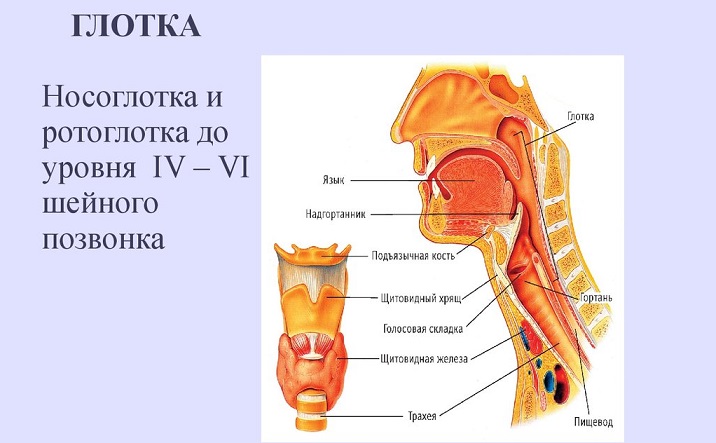
Now let's move on to the larynx, which is another component component of the throat. The larynx in the body is located inside the throat. In front of the larynx, there are hyoid muscles, and on top above it - a hyoid bone. The larynx from two sides is surrounded by the thyroid gland, and its rear part is adjacent to a sip, with its laryngeal part. All described organs can be considered in the figure:
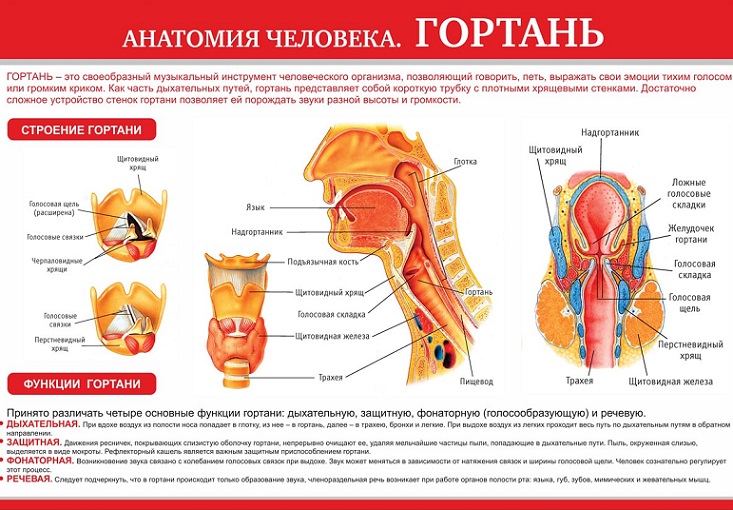
The entire muscle system of the larynx is divided into three main muscle groups. Each of them is responsible for its functions, respectively: tension, expansion and compression of all the corresponding muscles.
At the front of the larynx is the nastrian, and from two sides are formed in the form of wedge -shaped tubercles of sculpted folds. In the back of the larynx, there are drawn -shaped rolled -shaped cartilage. Inside, the larynx consists of: repentant and interventricular departments, as well as vestibule.
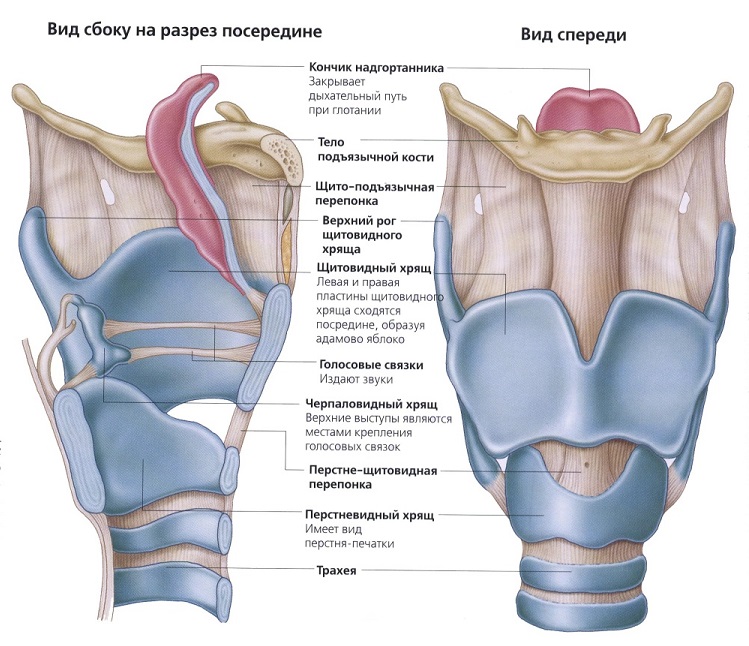
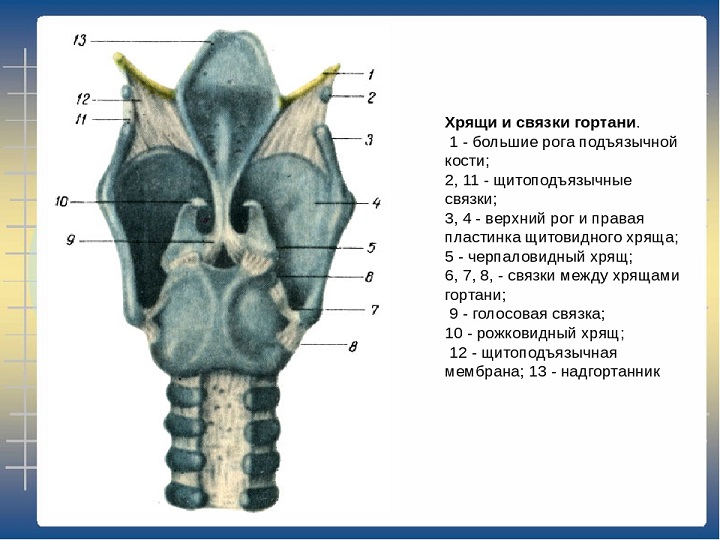
Accordingly, the echoing region is connected to the trachea, and the interventricular department is a narrow area between the waste folds and vocal cords. The eve begins in the area of \u200b\u200bthe dome, stretching to the folds, between which the heating gap is located.
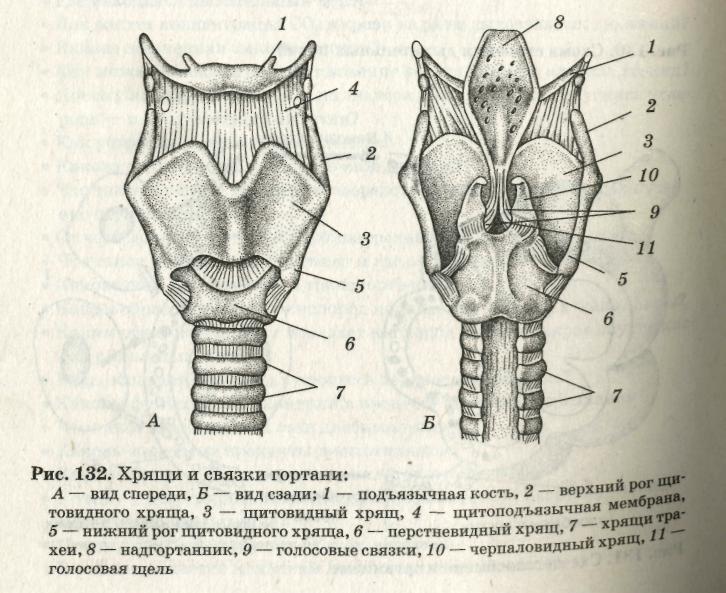
With the help of a larynx, we can breathe and speak, and it also performs a protective function. All its functions are connected with each other and perform general coordinated work: air flows have the opportunity to move into the lungs, while their direction is regulated accordingly. The flow of oxygen is regulated and directed by compression and expansion of the voice gap, and the protective function is ensured by the operation of the ciliated epithelium.
It should also be noted that the throat, nose and ear have an important relationship with each other. They are located in the human body next to each other and are united physiologically. Moreover, the work of one body can affect the work of another.
Diseases, injuries and pathologies associated with the throat: List
A list of diseases and ailments that a human throat may be subject to:
- Scleroma
- Tonsillitis
- Suffocation
- Intoxication by alkali
- Pharyngitis
- Injuries of mucous membranes
- Laryngospasm
- Lart tuberculosis
- Throat cancer
- Swelling of the larynx
- Phlegmon
- Laryngitis
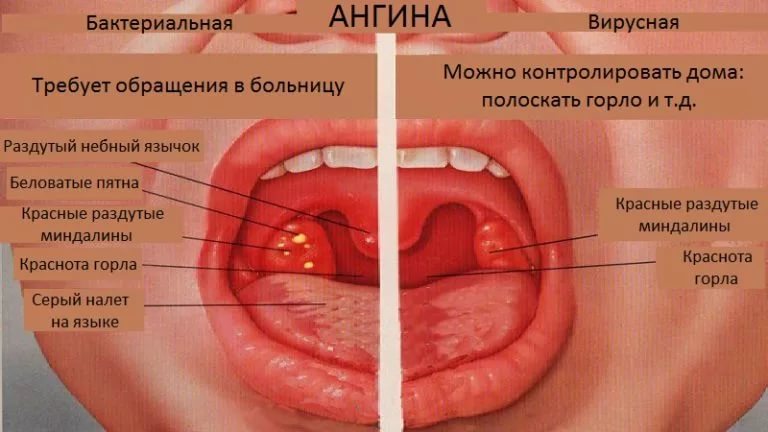
- Angina
- Intoxication with acid
- Burns of the mucous membranes
- Damaged throat
- Paratonsillitis
- Diphtheria
- Stenosis of the larynx
- Fracture of the cartilage
- Pharyngomycosis
- Injury
- Retropharyngeal abscess
- Hypertrophied adenoids
- The abscess is parafarinal
Factors affecting sore throat:
- Scarlet fever
- Smoking
- Inhaling dust
- Flu
- Inhaling smoke
- Whooping cough
- Acute respiratory diseases
Video: Throat Build