Everyone should know the symptoms of acute tonsillitis. This article describes the types of sore throats and their characteristics.
Contents
- Classification of sore throats: by localization, type of pathogen, type, time of appearance, photo
- The etiology of tonsillitis
- Types of sore throats and their characteristics in adults and children: a table with general clinical symptoms
- Angina: treatment, antibiotics, which drugs for sore throat are suitable for a child, an adult?
- Is there a viral sore throat: what is the causative agent, virus?
- Angina prevention
- Video: Purulent sore throat. How to treat chronic tonsillitis?
Angina is an infectious disease of an acute nature, in which the palatine tonsils (“Tonsilla” in the Latin language - “tonsil”) occurs. It is the tonsils that are the first line of protection in the hit of pathogens through the oropharynx. As a result, with the development of angina, a characteristic manifestation is observed: severe pain during swallowing. What is the classification of this disease, etiology and how is treatment performed? Look for answers to these and other questions in this article.
Classification of sore throats: by localization, type of pathogen, type, time of appearance, photo
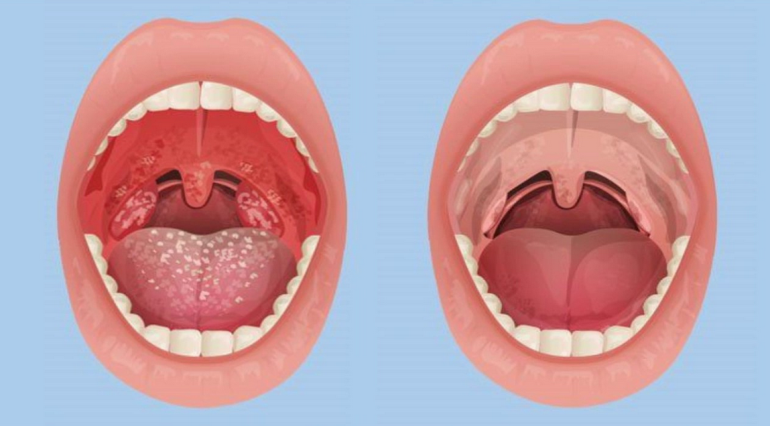
Classification of sore throats is performed according to different parameters: by localization, type of pathogen, type and time of appearance. Read more:
By location or localization, they distinguish:
- Nasopharyngeal
- Lingual
- Laryngeal
- Tonsillitis tonsils
The correct determination of the location of the pathological process contributes to an unmistakable diagnosis, as well as the prescription of timely and correct treatment.
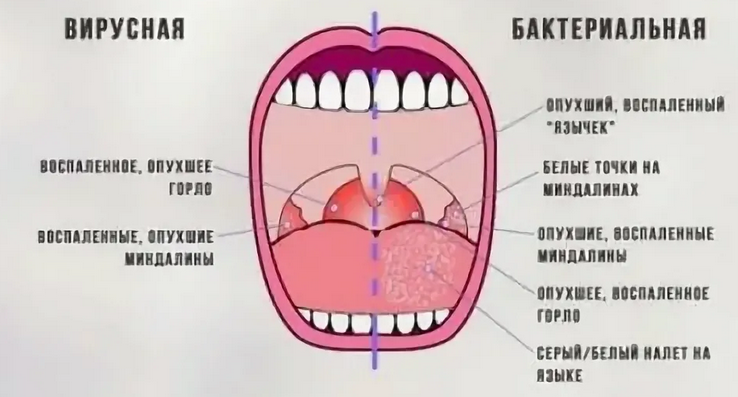
Depending on the type of pathogen:
- Bacterial
- Viral
- Fungal
- Mixed (viral-bacterial)
Before prescribing treatment, it is necessary to know exactly what form it is according to this classification. The definition can be made by sowing biomaterial from the oropharynx, as well as by clinical signs and symptoms.
It is worth knowing: Using drugs of a wide spectrum of action can give complications in the form of intoxication of the body. Therefore, only a doctor should be prescribed treatment.
Clinical classification - type:
This separation is based on a different state of the mucous membrane of the pharynx. Also on such clinical features as temperature, the degree of inflammatory process and on the results of laboratory tests. By type of sore throat there are:
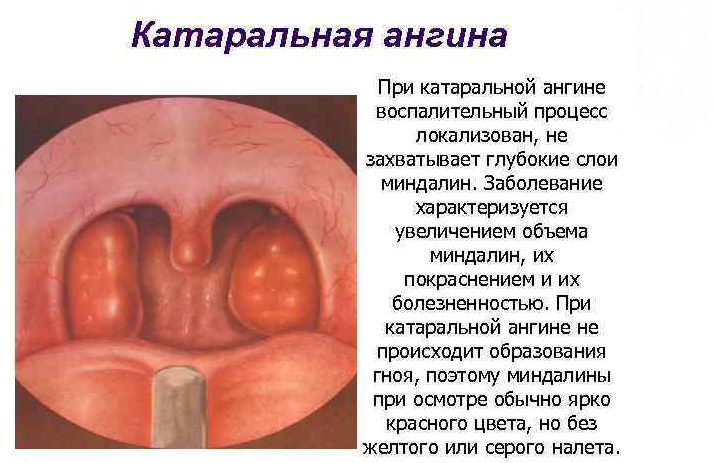
Catarrhal:
- The tonsils are affected in surface areas.
- The cause of development can be bacteria from the kind of staphylococci and streptococci, the number of which grows mainly with pathologies of the teeth and organs of the upper respiratory tract.
- The beginning is sudden, with a temperature raising to the mark 37.5 ° C..
- The tonsils are red, hyperemic, loose. There is a plaque in the language of the language.
- In the blood test, minor changes are observed.
- Symptoms pass within 2 daysAfter that, this form can progress in follicular or lacunar sore throat.
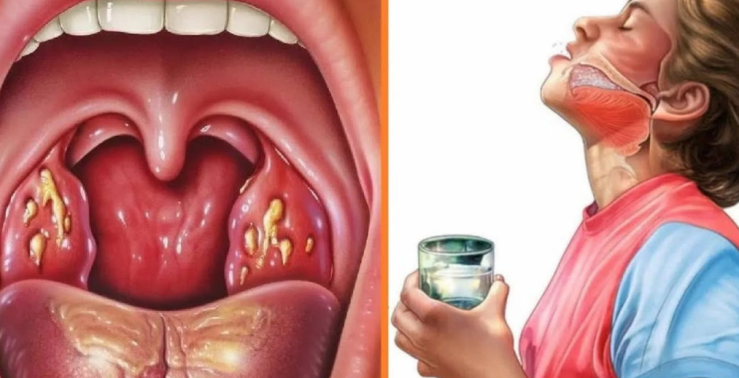
Folicular:
- The lesion of tonsils is deep.
- It is considered a heavier type.
- On the mucous membrane of the tonsils, a large amount of whitish-yellowed inclusions (suppurate follicles).
- The temperature rises up to 39-40 degrees.
- During laboratory diagnosis of blood test, leukocytosis is detected, the leukocyte formula is shifted to the left and an increase ESR up to 55 mm/h.
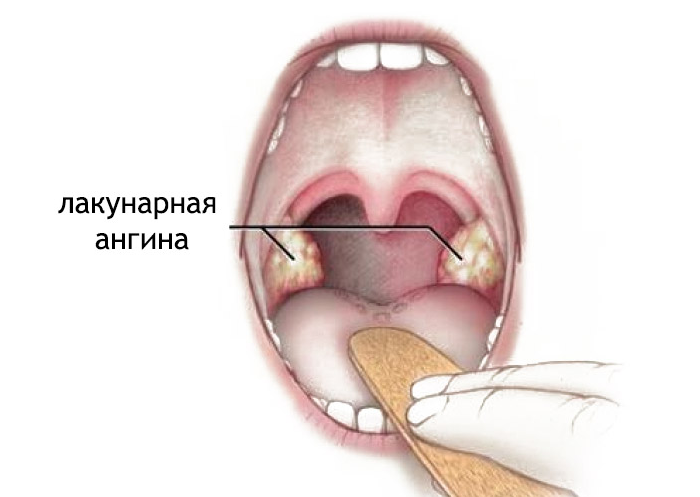
Lacunar:
- The presence of purulent plaque in the region of recesses on the surface of the tonsils.
- The gaps are expanded, the mucous membrane is red, edematous.
- The temperature increases up to 40 degrees.
- The results of laboratory diagnostics are similar to the values \u200b\u200bin a follicular form.
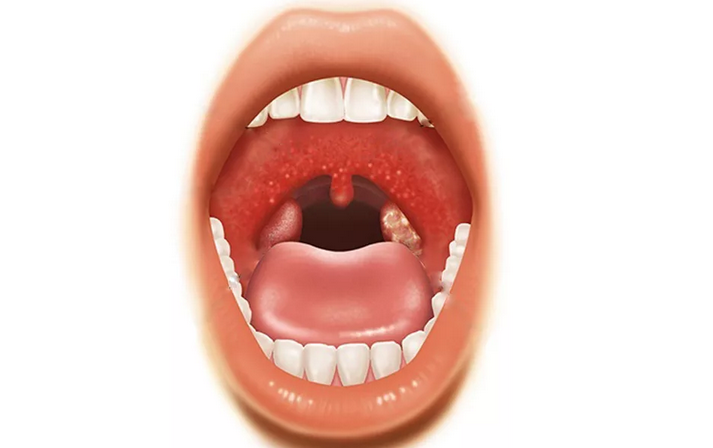
Herpetic:
- The reason is koksaki virus a.
- The first symptoms appear after 7-14 days After infection.
- The presence of herpetic rashes on the tonsils, a soft sky and the posterior wall of the pharynx, in the form of bubbles with serous contents.
- In most cases, children get sick.
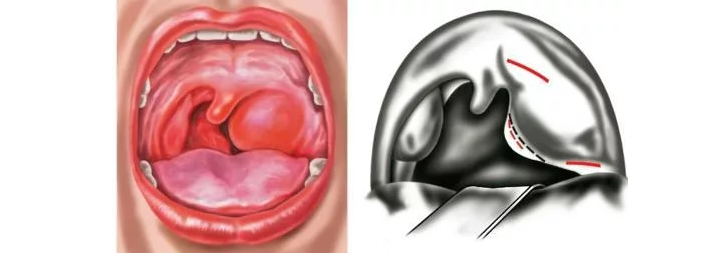
Phlegmonous:
- Complication of follicular and lacunar tonsillitis.
- The formation of an abscess in the tissues surrounding the palatine tonsil.
- The reason may be a throat injury to a foreign object.
- Mandatory presence of factors that affect the overall resistance of the body: stress, hypothermia, metabolic disorders.
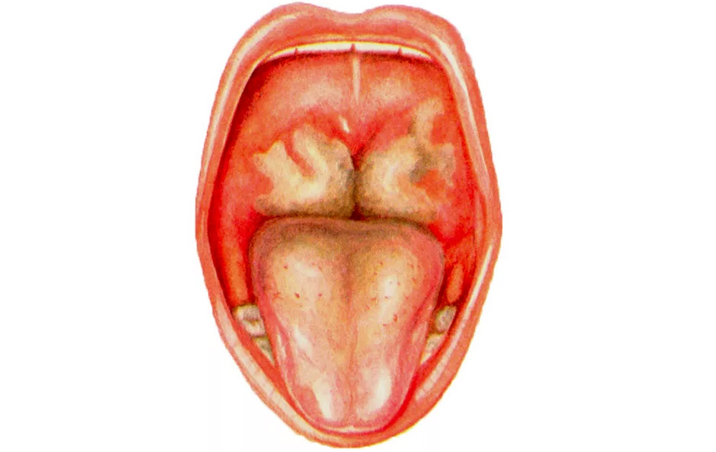
Fibrinous:
- It is also called fibrinous-smoke.
- It develops either as an independent inflammatory process, or as a complication of lacunar tonsillitis.
- The whitish plaque is present on the tonsils in the form of a single film.
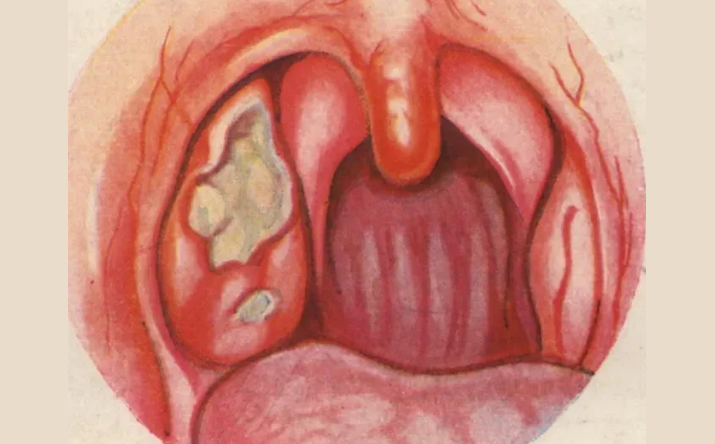
Ulcerative-smoke:
- The reason is the symbiosis of the spirochete of Vincent and the spindle -shaped wand. They are normally present in the oral cavity, but when weakened, the body cause this disease.
- On the surface of one tonsil necrosis with the formation of an ulcer.
- Without increasing temperature.
- In the analysis, moderate leukocytosis is observed.
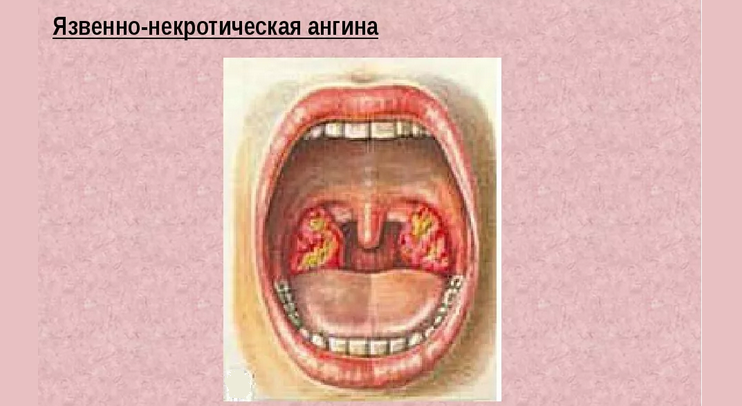
Necrotic:
- It proceeds most difficult and has pronounced symptoms.
- There are areas covered with grayish or greenish-yellow plate on the glands, spreading deep into the mucous membrane.
- The necrotic process often captures the back wall of the pharynx.
The time of occurrence is distinguished:
- Primary, which occurs either as a result of the first contact with the pathogen, or 3 years after the end of the acute period.
- Secondary (repeated), the infection develops after the previous one after a minor time (about 6 months).
Experts consider this separation to be conditional, but with the help of this classification you can determine which is precisely this tonsillitis: an acute or chronic form.
The etiology of tonsillitis
Etiology is an origin. There are many causes of tonsillitis. These are internal and external factors, as well as viruses, weakening of immunity, etc. Here is the etiology of angina:
- One of the frequent causes is bacteria, namely pyogenic streptococcus, less often staphylococcus (golden).
- Viruses: more often adenoviruses, less often enterovirus coksaki and herpesvirus.
- Mushrooms of the genus Candida. The fungal form often occurs after prolonged treatment with antibiotics.
- Spirochet Vincent In symbiosis with a spindle-shaped stick in the ulcerative form of the pathological process.
External and internal factors that contribute to the development of sore throats:
- Injury to the mucous membrane of the tonsils with foreign objects
- Chronic sinusitis
- Diseases of the oral cavity: caries, pulpitis, periodontitis
- Hypothermia
- Stress
- Vitamin deficiency with an unbalanced diet or gastrointestinal diseases
- Bad habits that negatively affect immunity - smoking, alcohol consumption in large quantities
A healthy person with a strong organism will not get a sore throat. When immunity falls, bacteria, viruses and various pathological processes settle on tonsils.
Types of sore throats and their characteristics in adults and children: a table with general clinical symptoms
Above, we described the types of sore throats according to the classification of doctors. Below you will find their characteristics in adults and children. Here is a table with common clinical symptoms:
| Types of sore throat | Symptoms | |
| Catarrhal | A feeling of dry mouth, Unpleasant sensations during swallowing, fever - in adults, the temperature may not increase, children are characterized by a significant increase in temperature, which often leads to vomiting, malaise, headache, The redness of the glands, with the progression of the pathological process on their surface, you can see the appearance of point bleeding, there is no purulent plaque. Improvements are observed after 5 days, subject to the doctor's recommendations. |
|
| Folicular | The sore throat often gives to the ear, Hypersalivation, temperature up to 39 degrees, nausea, vomiting, The lymph nodes are enlarged, painful on palpation, The mucous membrane of the tonsils is hyperemic, edematous, A white-yellow raid is in the shape of follicles. Subject to the prescribed treatment, improvement is observed in a week. |
|
| Lacunar | Body temperature rises to 40 degrees, malaise, The submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged and painful on palpation, Pain when swallowing, The palatine tonsils swell, on their surface a white or yellowish -colored plaque. Improvement occurs after 7 days of proper therapy. |
|
| Herpetic | Temperature rise, nausea, vomiting, weakness, malaise, Lymph nodes in the neck are enlarged, Reddish abscesses form on the surface of the tonsils. |
|
| Phlegmonous | The body temperature is critical. Strong intoxication, reduction of appetite, The defeat of the tonsils on the one hand: hyperemia, the soft sky is swollen, as a result of speech impairment. |
|
| Fibrinous (fibrinous-smoke) | Heat, chills, intoxication, the presence of a single white-yellow film that can capture space outside the tonsils, Signs of brain damage. |
|
| Ulcerative-film | Increasing body temperature to 38 degrees, The fetid smell from the oral cavity, Hypersalivation, The presence of a plaque in the form of films that are easily removed, as a result, ulcerative painful surfaces are formed. With high -quality therapy, treatment takes a week. |
|
| Necrotic | Fever, confused consciousness, nausea, leukocytosis, neutrophilia, The grayish plaque penetrates deep into the tonsils, has a staged structure, The affected area is compacted, Necrotic formations are spread to the back of the pharynx. |
|
Any of these types of sore throats should not be ignored. If there are signs of such a pathology, then you should urgently consult a therapist or Laura. In advanced cases, or when improvements do not occur, the doctor may decide to treat the patient in the hospital, in the infectious department.
Angina: treatment, antibiotics, which drugs for sore throat are suitable for a child, an adult?

There are 3 principles of treatment of tonsillitis:
Surgical intervention:
This method is used for constant relapse of infection, depending on the spread of the process, either partial or complete excision of the tonsils is performed.
Physiotherapeutic methods:
- Inhalation
- UHF
- Electrophoresis
- Magnetotherapy
- Phototherapy
Prescription of the course of medicines - What preparations for sore throat are suitable for a child, an adult? Detailed response:
- In the form caused by bacteria - antibiotics. Based on the results of the identification of the sensitivity of microorganisms to certain drugs, the most effective medications are selected. First of all, penicillins are considered: amoxicillin, in the presence of allergies - cephalosporins. In case of hypersensitivity for most beta-lactam antibiotics-macrolides.
- With a viral form - The use of antiviral and anti -inflammatory drugs.
- With a fungal form - antifungal agents.
Symptomatic drugs that are used in the treatment are also used:
- Antipyretic
- Antiseptics
- Preparations that reduce unpleasant sensations in the throat
The latter include sprays, resorption loafers and rinsing solutions, which are used hourly.
Features of symptomatic therapy in children:
- Rinse sage
- Chamomile
- Saline with soda
To prevent spasm of the larynx, kids up to 2 years It is not recommended to use sprays with antiseptics and drugs containing essential oils.
Is there a viral sore throat: what is the causative agent, virus?
Yes, viral sore throat exists. The causative agent is mainly koksaki virus arelated to the Enterovirus family. Adenoviruses can also play a significant etiological role. In this case, the lack of plaque or pustules on the tonsils is characteristic.
Angina prevention

In order to constantly be healthy and not getting sick with sore throats, it is important to carry out the right preventive measures. Since childhood, pediatricians advise parents to temper children, walk a lot in the fresh air and eat right, limiting sweets and fast food. Here's what else you need to do to increase immunity, both local in the throat and general, and not get sick with sore throat:
- Regular sanitation of the oral cavity.
- Timely detection and therapy of diseases of the organs of the upper respiratory tract (sinusitis, rhinitis) and organs of the oral cavity (caries, periodontitis).
- A balanced and diverse diet to maintain the necessary level of vitamins and trace elements in our body.
- Lack of bad habits.
- Daily physical activity in the air.
- Compliance with simple hygienic rules: washing hands, using only their personal hygiene items.
- Regular ventilation and cleaning using disinfectants in rooms.
Angina is a serious infectious disease that requires compulsory treatment under the qualitative supervision of a specialist. Remember this. Good luck!